Angular Sensors | Types and Space solution
- Posted by Alina Spuma,
- On September 29, 2020
- 0
Angular sensors (AS) are position devices that provide the displacement in angular degrees with respect to a fixed point or an arbitrary reference making them absolute or relative sensors. Combining position with time measurements, speed and acceleration can be calculated.
A wide range of position sensors available in the market are based on different technologies: resistive-base (potentiometers), magnetic and inductive sensors (hall-effect, eddy current sensors, resolvers) optical and electric encoders. Each technology has a series of advantages but also limitations. Choosing the proper technology depends on application requirements and is generally cost-dependent.
Angular Sensors Performances
Some of the main performances of the angular sensor are:
- Resolution: smallest significant increment that can be detected
- Accuracy: how far the measured value is from the true position value
- Repeatability: the ability to obtain the same result when measuring at different time
- Measurement range: angular travel that can be measured.
In addition, environmental conditions as increased temperature range, under-vacuum operation and radiation hardness must be considered. Low power consumption and standard electrical/mechanical interfaces are demanded easy integration.
Space Applications
In space applications, angular sensors are needed for position control of mechanisms included in most of the space missions:
- SADM (solar array drive mechanism)
- APM (antenna pointing mechanism)
- Linear and rotary motion actuators
- Scan mechanisms
- Restrain and release mechanisms
- Hingers / pivots.
The required performances when choosing an angular sensor may differ from one application to another.
For instance, high performances sensors are required for very accurate scanning/pointing mechanisms in scientific payloads and telecom equipment. These sensors can provide accuracies of 24 bit (0.07arcsec).
Instead, for a solar array pointing mechanism or a restraint and release mechanisms, accuracies of 0.5º or 0.1º may be enough.
Based on their accuracy angular sensors may be classified into two categories: medium-low accuracy sensors and high-performance encoders.
Current Technologies for medium-low accuracy AS
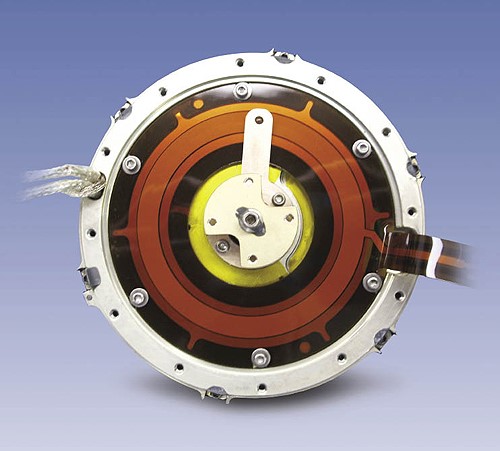
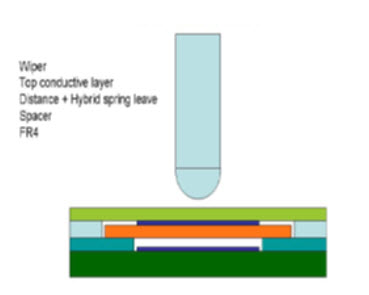
POTENTIOMETERS are by far the most common use of medium-low resolution sensors. They consist of a wiper moving over a conductive or resistive track and provide an output voltage proportional to the change in resistance. The extended use in space mechanisms is enhanced to their easy to use, the low power consumption and relatively low costs. Some models provide resolutions of 0.1º and even 0.05º, but the functional range is limited to around 357º (dead zone of 3º). Lifetime is limited due to wearing. The commonly reported failures are signal noise and drop-outs.
Some improvements were reported by Moog QuieSenseTM noise-free membrane potentiometer. The technology is based on SENSOFOIL® and consists of several layers separated by spacers. These layers are connected to each other through the pressure generated by the Vespel wiper. Wearing does not affect the performance characteristics of the potentiometer as the wiper slides on the external Kapton surface.
Other angular sensors technologies
Magnetic and inductive sensors are also used for position sensing. The main disadvantage is their sensitivity to electromagnetic interferences.
MAGNETIC AND INDUCTIVE ANGULAR SENSORS
| wdt_ID | Technology | Functioning principle | Performances | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hall sensors | A moving part is linked to a magnet housed with a sensor shaft forming a Hall element. The magnet moves which leads to the formation of magnetic field and hence Hall voltage. | Resolution of 0.5º Functional range 360 º with multi-turn allowable rotation. The contactless technology reduces the wear out and increase the lifetime | Sensitive to electromagnetic interferences |
| 4 | Resolvers | Variable transformers operate by magnetic induction. | Accuracies around 0.02º Very good performances under extreme temperatures, humidity, vibration and shocks | Sensitive to electromagnetic interferences |
Current technologies for High-Performances AS
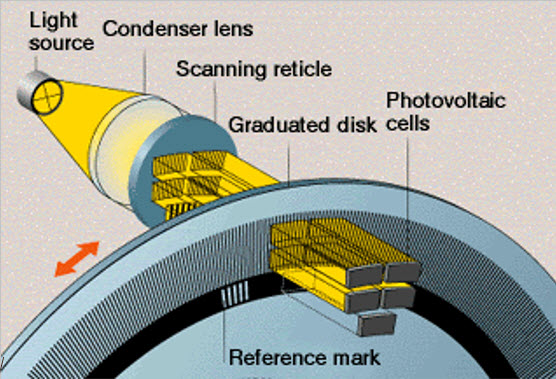
High-performance sensors are needed for very accurate scanning/pointing mechanisms in scientific payloads and telecom equipment. Optical and electrical encoders generally respond to this demand. These sensors costs are significantly increased and performance-dependent. The integration is complex as they are sensitive to mechanical tolerances and misalignment. The optical sensors suffer degradation of the performances due to radiation and the exposure to increased temperature range. Codechamp optical encoder is the only one with space heritage. These encoders provide resolutions as high as 24 bit (0.07arcsec).
Optical sensors are based on photoelectrical scanning. They consist in a shaft mechanically coupled to an input driver which rotates a disc rigidly fixed to it. A succession of opaque and clear segments is marked on the surface of the disc. Light from infrared emitting diodes reaches the infrared receivers through the transparent slits of the rotating disc. Complex electronics are needed for angular position calculus.
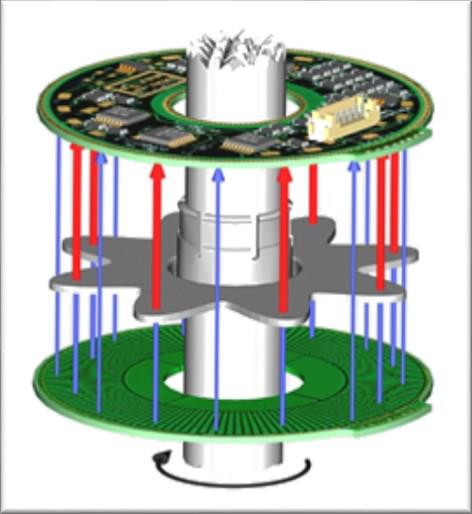
Netzer Rotary Electric Encoder™ include a space/time modulated electric field inside a shielded space. The total field is integrated and converted into a signal current which is processed by onboard electronics to provide DC output signals proportional to the sine and cosine of the rotation angle. Digital output is provided by external conditioning electronics. They have a resolution of 19 bit (0.0006º) and perform in large temperature range but are sensitive to radiation. Netzer sensors were used by ESA in a demonstrator of a robotic arm.
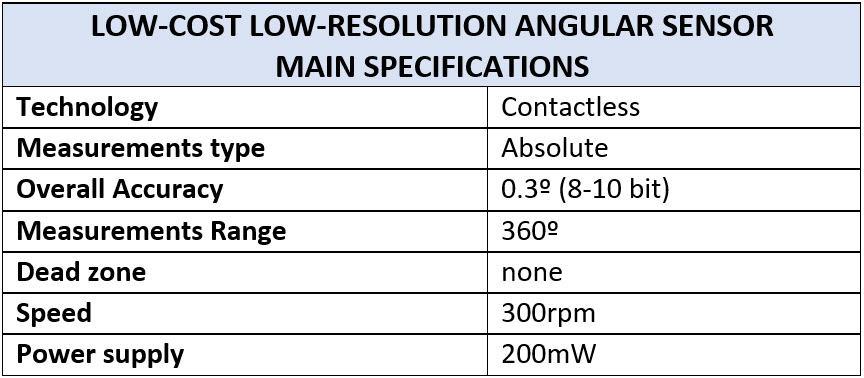
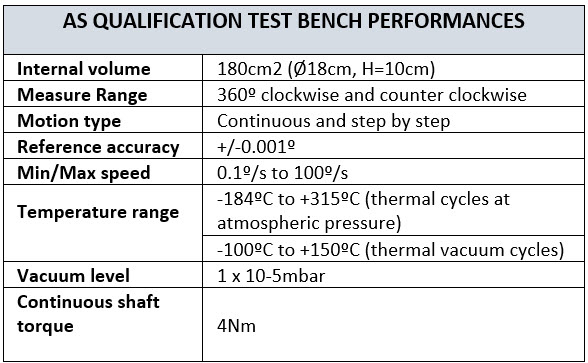
Low-Cost Low-Resolution position Sensor (ESA ITT 9775)
Alter Technology and EMXYS are currently involved in ESA ITT 9775 which focuses on development and characterization of low-cost angular sensors for space mechanisms as an alternative to potentiometers without their noise issues and for a competitive cost.
The goal of this activity is to design, manufacture and test a breadboard model (BBM) of a position sensor targeting low cost, low accuracy (8 to 10 bits) and high reliability. The main specifications of the sensor being developed are:
EMXYS Capacitive Null-Mode displacement measurement technology
It consists of varying the capacitance by changing dielectric constant by moving a dielectric material between two fixed plates or with an overlapping area between the moving plate and the fixed part. The contactless technology responds to the existing need for long-life mechanisms: no contact between rotor and stator, no degradation of performance due to wear.
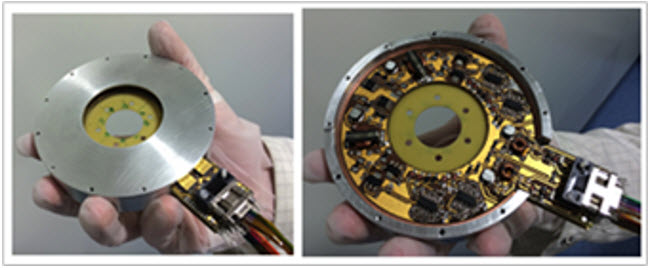
EMXYS contactless angular sensor
Contactless sensor and can provide both analogue or digital output. It used ECSS space-qualified materials and components responding to the harsh environmental conditions a space application may demand.
For critical instruments where a failure may jeopardize mission success, the device can be provided in full redundancy mode.
References:
[1] Harmonization Workplan 2018-ESA_IPC2017
[2] Angular position sensors for space mechanisms, Nicolas Steiner, Dominique Chapuis
[3] NETZER AN01_Electrical-Encoder-concept-2016-03
[4] Resonant_inductive_vs_resolvers, Cambridge IC
[4] Codechamp http://www.optical-encoders.eu/optical-encoder.html
[5] Honeywell https://sensing.honeywell.com/sensors/non-contact-hall-effect-rotary-position-sensors
[6] ESA ITT 9775 Work statement
- ANGULAR SENSORS MEASUREMENTS - February 18, 2022
- Mars 2020 SuperCam Calibration Target (SCCT) - February 15, 2022
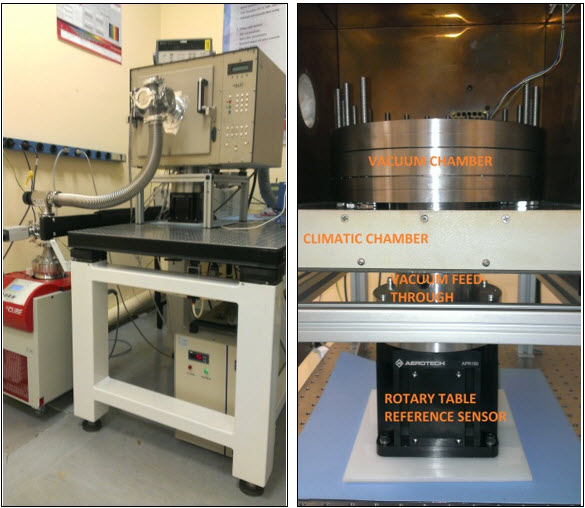
- Angular Sensors Measurements in Vacuum and Temperature - December 1, 2021



0 comments on Angular Sensors | Types and Space solution