Lumped Element L-C Filters Design and Characteristics
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On June 26, 2024
- 0
The Basics of Lumped Element L-C Filter Construction
In general, lumped element filters are passive filters constructed using the appropriate number of inductors (Ls), capacitors (Cs), and resistors (Rs) to meet the specific filtering needs of a particular application.
At the most basic level, lumped element filters can be constructed from a collection of simple L-C resonators, as shown in Figure 1.
The resonators used in the filter will create poles and zeros in the frequency response. A zero occurs when the function tends to zero, and a pole occurs when the roots that make the function tend towards its maximum function.
By understanding how poles and zeros function, we can construct resonators using Ls and Cs and place them where we need them to be to control the frequency response tightly.
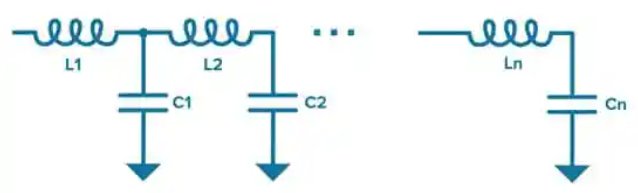
Figure 1. An example of a generic lumped element L-C filter structure
Lumped Element Filter Characteristics
Lumped element filters offer small size at low frequencies that are not achievable with common ceramic, cavity, or waveguide implementations. Additionally, lumped element filter designs are highly customizable both in terms of electrical performance and mechanical and thermal characteristics.
This is because we have a high level of control in terms of component and material choices as well as assembly techniques. For example, a lumped element filter can be constructed with withstand temperature and input power ranges that may not be possible with alternative resonator technologies.
What Filter Types Can Be Built Using a Lumped Element Construction?
All the usual filter types, including lowpass, highpass, bandpass, and band-reject, can be implemented in a lumped element format. As discussed in more detail in the Basic Filter Circuits Explained article, lowpass and highpass elements are relatively simple to develop, and bypass filters can be pretty easily constructed by combining the two behaviors.
Lumped Element Filters Capabilities
Lumped element filter frequency and bandwidth range available by Knowles Precision Devices are shown in Figure 2 below.
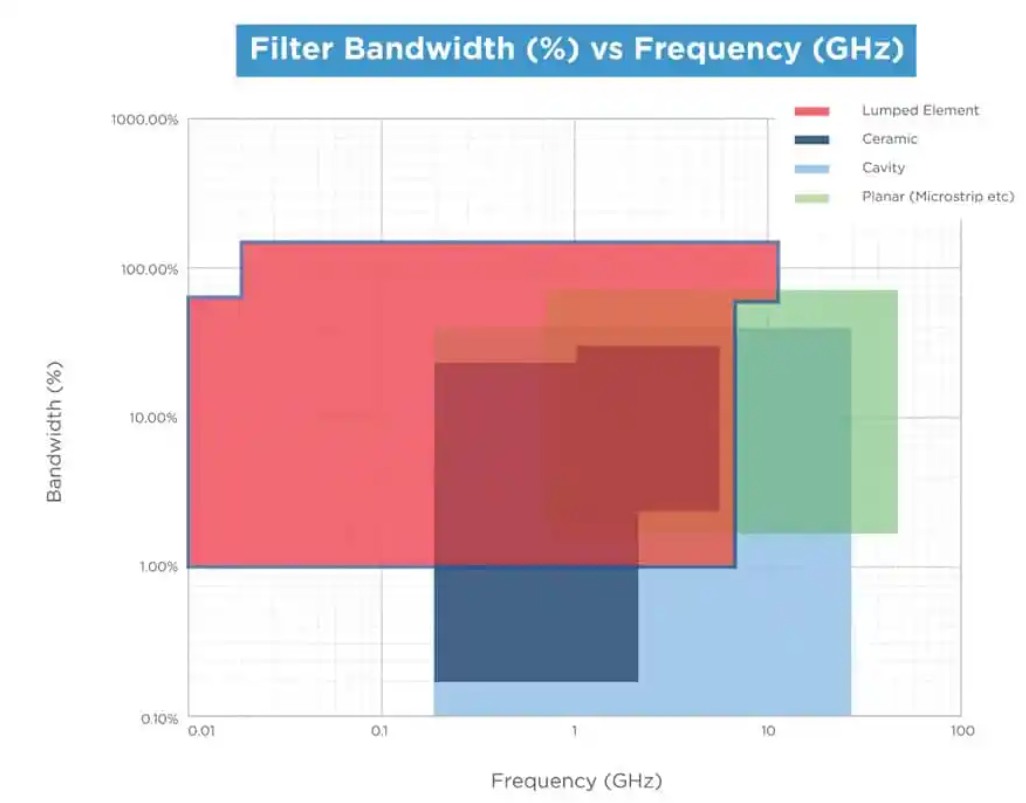
Figure 2. Lumped element filters frequency and bandwidth range; source: Knowles Precision Devices
Lumped element filters can be customized to operate reliably in high-power, high-temperature, and harsh environmental conditions. More specifically, lumped element filters can be designed with the following specifications:
- Bandpass filters with narrow to moderate bandwidths (1 per cent FBW to 70 per cent FBW) and a Center Frequency (Fo) from 10 MHz to 7 GHz
- Bandpass filters with an extra wide bandpass bandwidth (70 per cent FBW to 175 per cent FBW) and a Fo of 20 MHz to 11 GHz
- Lowpass filters from 10 MHz to 22 GHz
- Highpass filters from 10 MHz to 10 GHz
- Band reject filters from 20 MHz to 6 GHz that can be narrow band or wide band from 10 MHz to 6 GHz
Source: Passive Components Blog
- Miniature RF Connectors - April 29, 2025
- Miniature RF Connectors for high-performance testing - April 24, 2025
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025

0 comments on Lumped Element L-C Filters Design and Characteristics