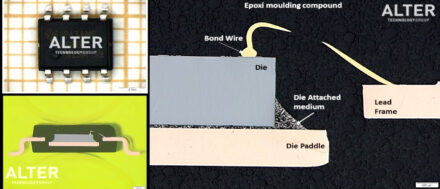

Cross Sectioning for Schottky Diodes
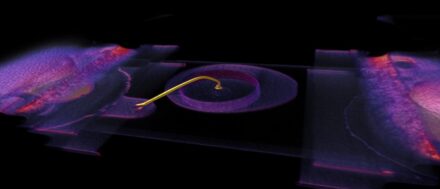
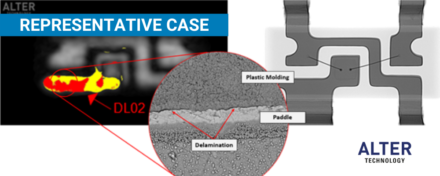
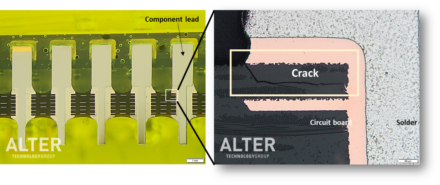
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
Cross Sectioning for Schottky Diodes
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
8 results found for Schottky/RF-Microwave Diode/Diode/Discretes
Part reference
Quality level / QPL
Package
Power Dissipation [Max]
TID (krads)
Forward Current [Max]
Total Capacitance [Max]
Unit price
Lead time
ESCC C
Not qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
HPAC-140
70mA
ESCC C
Not qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
120mA
4pF
ESCC
Not qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
HPAC-140
70mA
ESCC
Qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
120mA
4pF
ESCC C
Not qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
70mA
2pF
ESCC
Qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
120mA
4pF
ESCC
Qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
70mA
2pF
ESCC
Qualified
ESCC QPL
Surface Mount
T1
0,25W
70mA
2pF
Part validation activities
Cost & Activity Matrix