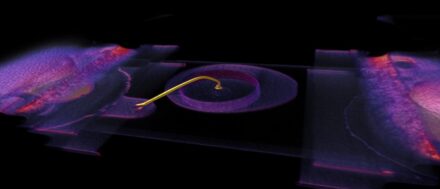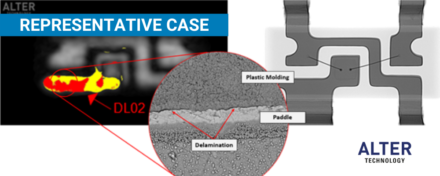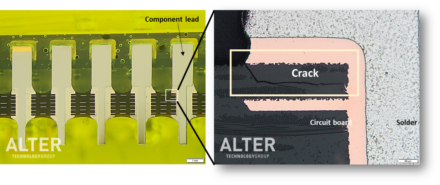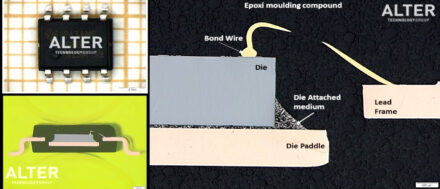

Cross Sectioning for Power Transformers
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
Cross Sectioning for Power Transformers
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
3946 results found for Power Transformers/Transformers
Part reference
Quality level / QPL
Package
Type
Power Rating
Unit price
Lead time
LEVEL M
Not qualified
QPDSIS-27
Through Hole Mount
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
1,5VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Point to Point Wiring
Toroidal
POWER SINGLE PHASE
50VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Through Hole Mount
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
25VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Point to Point Wiring
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
120VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Point to Point Wiring
Toroidal
POWER SINGLE PHASE
1,5VA
LEVEL M
Not qualified
QPDSIS-27
Point to Point Wiring
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
24VA
LEVEL M
Not qualified
QPDSIS-27
Through Hole Mount
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
25VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Point to Point Wiring
Toroidal
POWER SINGLE PHASE
3VA
LEVEL M
Not qualified
QPDSIS-27
Through Hole Mount
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
6VA
LEVEL M
Qualified
QPDSIS-27
Through Hole Mount
Box
POWER SINGLE PHASE
16VA
Part validation activities
Cost & Activity Matrix