
Cross Sectioning for Logic SCAN ICs
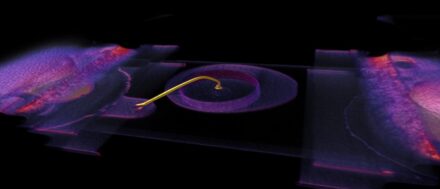
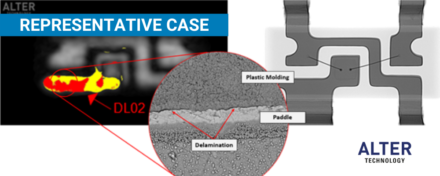
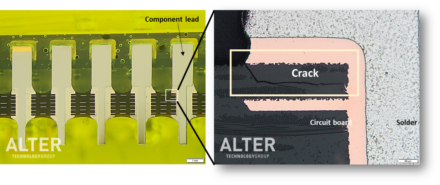
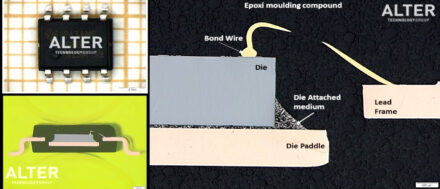
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
Cross Sectioning for Logic SCAN ICs
The cross-sectioning process provides access to the device internal structure, its materials and design. Electronics components are often subjected to cross-sectioning to detect the defects that could not be found using other testing techniques. Cross-sectioning typically involves three discrete steps: mounting the sample in a block of epoxy resin to form the specimen, grinding or cutting the specimen and finally polishing the exposed surface. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
41 results found for SCAN/Logic/Digital/Microcircuits
Part reference
Quality level / QPL
Package
Type
TID (krads)
SEE (MeV/mg/cm2)
Number of Bits
Unit price
Lead time
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CFP-56
Transceiver
18-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQLCC-28
Transceiver
8-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQLCC-28
Transceiver/Register
8-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-24
Buffer
8-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQLCC-28
Inverting Buffer
8-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-28
4-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-24
Inverting Buffer
8-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CFP-56
D-Type Flip Flop
9-Bits
QML Q
Not qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQFP-68
Transceiver/Register
18-Bits
QML Q
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQFP-68
Transceiver
18-Bits
Part validation activities
Cost & Activity Matrix