
Displacement Damage Test for Analog Multiplier
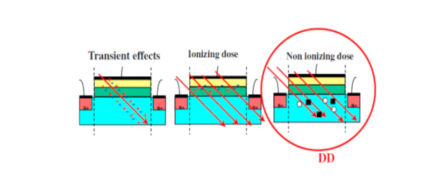
Displacement Damage is the result of nuclear interactions, typically scattering, which cause lattice defects. This effect degrades minority carrier lifetime; a typical effect would be gain degradation and leakage current in bipolar transistors. Displacement damage depends on the loss of non-ionizing energy , i.e. energy and momentum transfer to lattice atoms, which depends on the mass and energy of the incident quanta. A simple measure like for ionizing radiation is not possible, so displacement damage must be specified for a specific particle type and energy. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
Displacement Damage Test for Analog Multiplier
Displacement Damage is the result of nuclear interactions, typically scattering, which cause lattice defects. This effect degrades minority carrier lifetime; a typical effect would be gain degradation and leakage current in bipolar transistors. Displacement damage depends on the loss of non-ionizing energy , i.e. energy and momentum transfer to lattice atoms, which depends on the mass and energy of the incident quanta. A simple measure like for ionizing radiation is not possible, so displacement damage must be specified for a specific particle type and energy. >> Read more
EEE Parts Results Page
21 results found for Analog Multiplier/Signal Acquisition-Conditioning/Microcircuits
Part reference
Quality level / QPL
Package
Unit price
Lead time
QML V
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
TO-100
883
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
TO-100
JAN B
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
TO-100
883
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Surface Mount
CQLCC-20
JAN B
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
TO-100
QML H
Not qualified
QPDSIS-38534
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-14
883
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-14
QML V
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-14
QML H
Not qualified
QPDSIS-38534
Through Hole Mount
CDIP-14
883
Qualified
QPDSIS-38535
Through Hole Mount
TO-100
Part validation activities
Cost & Activity Matrix