Dissipation Factor (DF) measures energy loss in capacitors, indicating efficiency, especially in AC circuits and high-frequency applications.
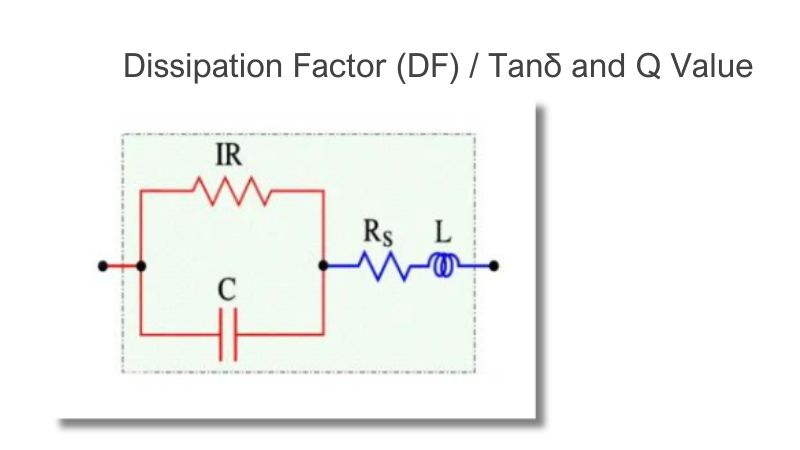

Dissipation Factor (DF) measures energy loss in capacitors, indicating efficiency, especially in AC circuits and high-frequency applications.
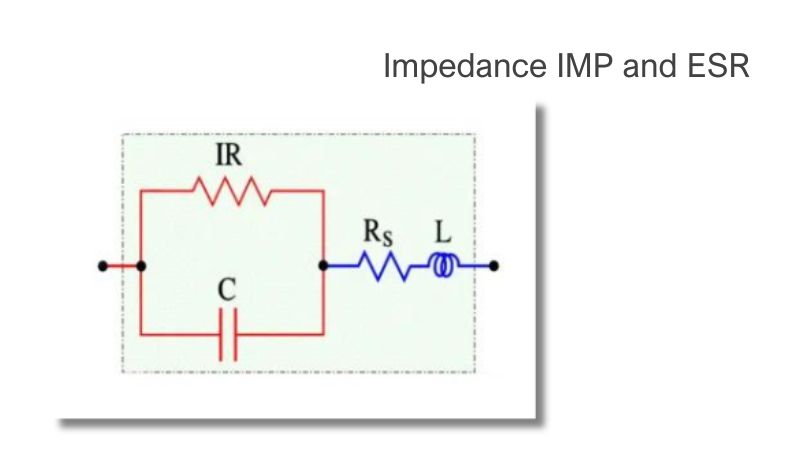
Capacitor losses explained through ESR, impedance, dissipation factor, and quality factor, affecting AC circuit performance across frequencies.

Film capacitor technologies cover AC/DC applications, including power transmission and renewable energy, with insights into dielectric materials like polypropylene and PET.

The dielectric constant measures a material’s capacity to store energy in a capacitor, affecting capacitance and energy storage efficiency.
Polystyrene capacitors, valued for low losses, are being replaced by PPS, which offers higher temperature resistance, especially in SMD designs.
Polycarbonate PC capacitors, once dominant in precision applications, are now being replaced by polypropylene due to manufacturing decline.

Polypropylene (PP) capacitors provide low dielectric losses and temperature stability, making them ideal for AC, pulse, and interference suppression applications.

The article covers the differences between polyester PET and PEN capacitors, temperature resilience, and best practices for preventing shrinking during soldering in SMD designs.
Paper capacitors use impregnated paper dielectrics to prevent corona effects, evolving with plastic films for improved performance in power and RFI applications.
Film and foil capacitors use plastic dielectrics like polyester and polypropylene, offering self-healing and stability for power and safety applications.
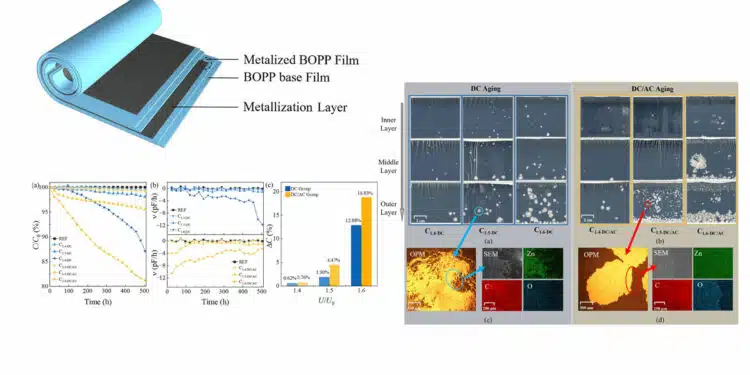
This article investigates the failure mechanisms of metallized film capacitors (MFCs) when subjected to DC fields with superimposed AC harmonics.