This article presents a detailed comparison of the rejection thresholds defined by major standards—IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020, ESCC 25200, MIL-STD-1580, and NASA’s PEM-INST-001—for defects detected through Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM). By analyzing how each specification addresses anomalies such as delamination, cracks, voids, and contamination, this overview highlights key differences in acceptance criteria and the need for complementary tests to assess actual reliability risks. The goal is to support more consistent and informed decision-making in quality screening for high-reliability electronics.
Rejection criteria comparison
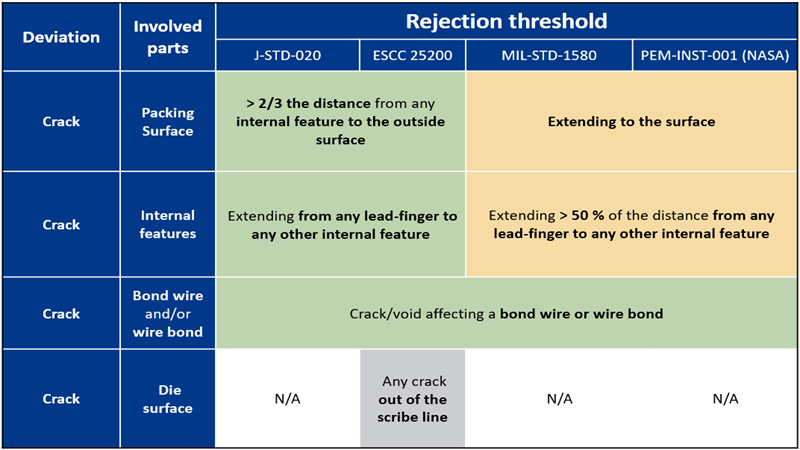
Crack extending from internal features

Void affecting a bond wire

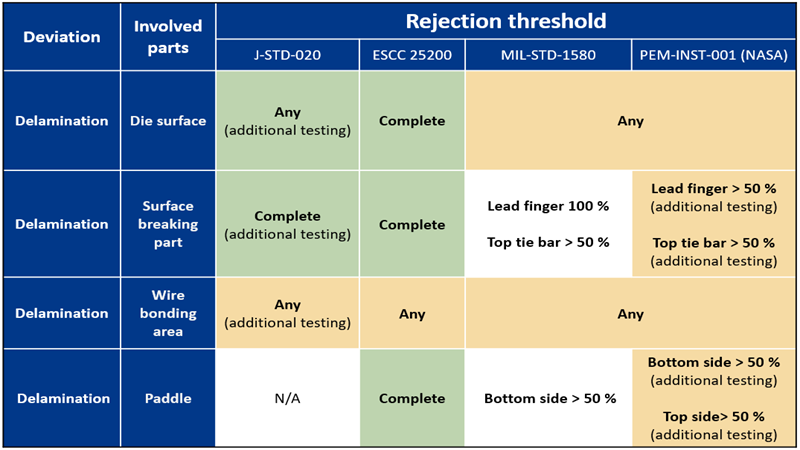
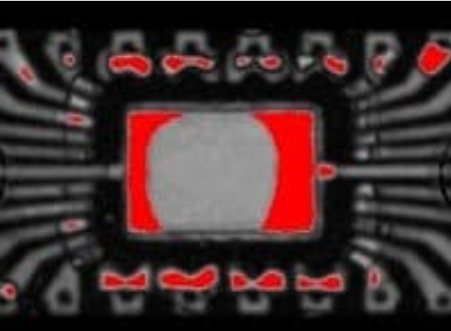


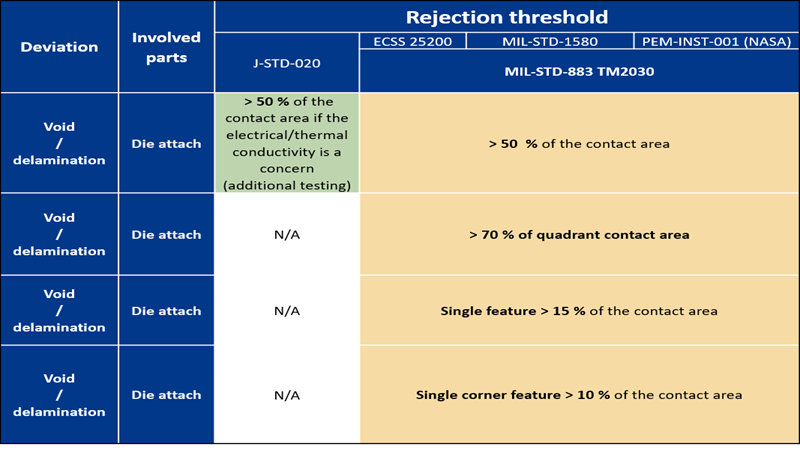
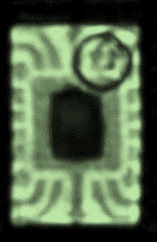
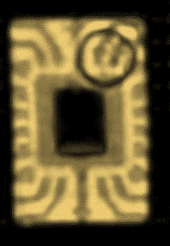

Additional testing: This deviation is considered as a reliability concern and additional tests must be conducted to check the system performance. From the point of view of the SAM inspection, such deviations do not comply with the acceptance criterion
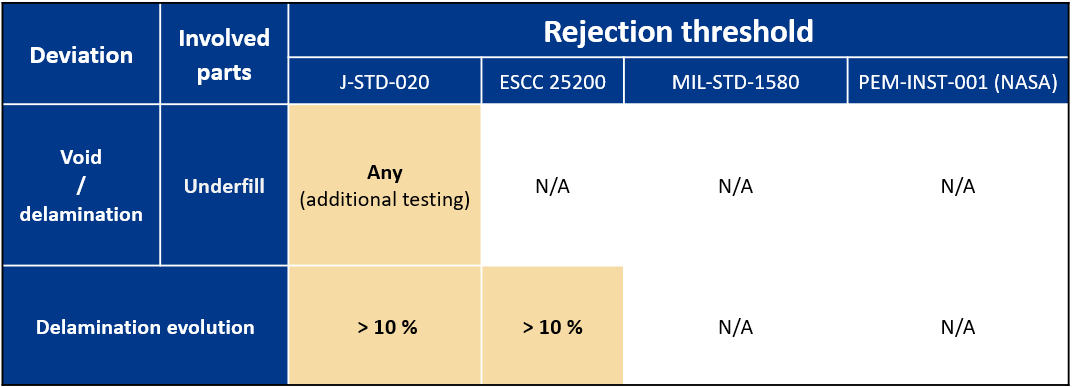
Additional testing: This deviation is considered as reliability concerns and additional tests must be conducted to check the system performance. From the point of view of the SAM inspection, such deviations do not comply with the acceptance criterion.
Conclusion
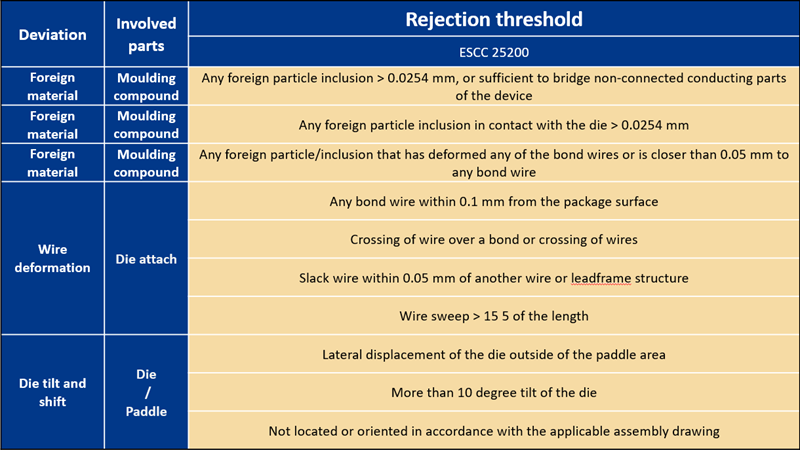
The most frequently observed issues are addressed by all the analyzed specifications. Nonetheless, there are remarkable differences such as:
- The rejection thresholds
- Only in some methods are additional tests and/or inspections used to confirm suspected results and to further evaluate the actual impact on the system’s performance, reliability and or durability

Author:
Francisco Javier Aparicio Rebollo
