We have previously talked about the revolution that the Space business is currently experiencing, with New Space being a key player in it. To adapt to the new trends and necessities of the market, the main component manufacturers are releasing new type series to cover this gap.
In this sense, Microchip, a global leader in the manufacture of FPGAs for Military and Space use has planned to release intermediate quality levels FPGAs for New Space projects. This will allow a reduction in cost of the component and lead time on FPGAs.
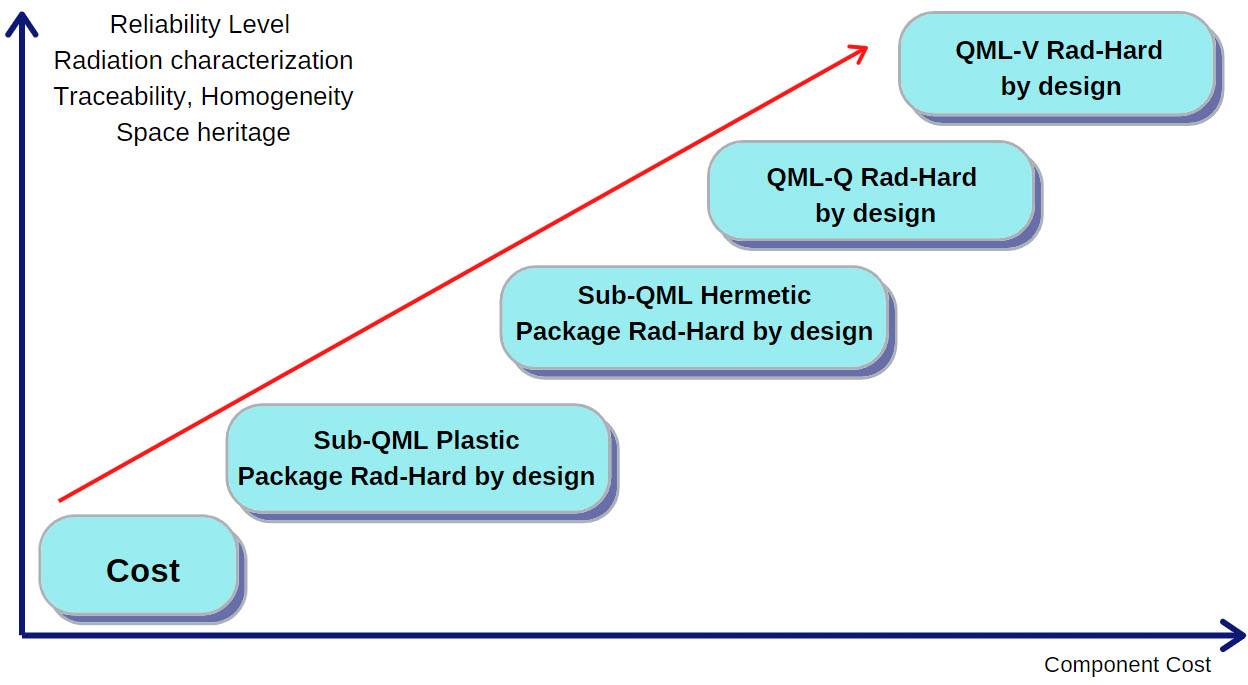
Two Sub-QML Radiation Tolerant series are planned:
- Ceramic package, Sub-QML Radiation Tolerant, Hermetic
- Plastic Package, Sub-QML Radiation Tolerant, Hermetic
While cost and lead time reduction will come from the reduction or elimination of QML testing and documentation, the possibility of having space heritage, manufacturer technical support, radiation and reliability data and lot traceability will make these parts an attractive alternative for those users involved in New Space constellations.
The main characteristics these parts will include are:
- Ceramic – Reduced Flow and Mil Temp Hermetic
- Plastic Package – Military temperature
- Radiation hardened by design
- No screening will be performed but 100% Electrical Measurements at three temperatures.
- Full traceability, homogeneity & CoC are granted
- Single base line
Three different sub-QML flows are added to Microchip portfolio Sub-QML screening flows:
- Mil-Ceramic
- Mil-Plastic
- R-flow (Reduced flow)
While on Mil-Plastic and Mil-Ceramic flows screening or radiation testing is not performed, each wafer lot is TID tested and same test and screening as B-Flow is performed on R-flow.
More information related to Microchip Space Products and Microchip Rad-Tolerant FPGAs