Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA) is a systematic, logical, detailed examination of EEE parts at various stages of physical disassembly. This activity is performed in order to verify that the manufactured lot quality is in accordance with the detailed specification and project requirements.
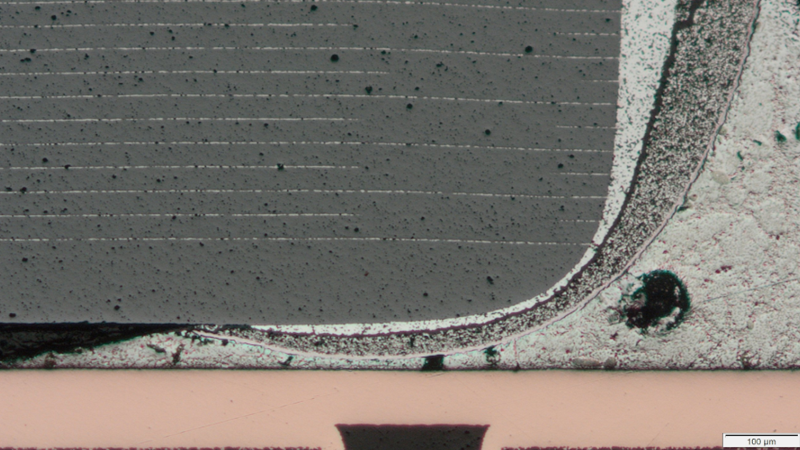
In a DPA, parts are examined for a wide variety of design, workmanship, and processing problems that may not have been present during the previous inspection, test, and screening activities performed by the component manufacturer.
Anomalies and defects detected through DPA could, at some later date, cause degradation or failure of the system in which the devices are to be employed. DPA is conducted on samples taken randomly from the lot and consists of a series of various tests and inspections depending on the type of component and package. Among them:
- X-ray Examination
- External Visual Inspection
- Seal tests (Fine& Gross leaks)
- Particle Impact Noise Detection (P.I.N.D)
- Solderability
- Internal Visual Inspection
- Bond Pull
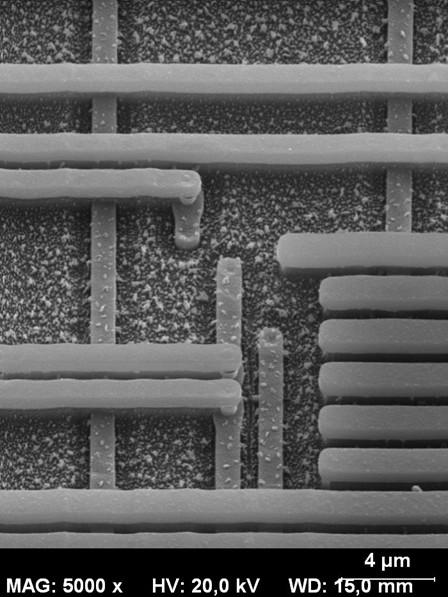
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Die Shear
The DPA process can be performed in accordance with MIL-STD-883, MIL-STD-750, and MIL-STD-1580.

RF filter failure detected during the internal visual inspection which is a part of the cross sectioning process.
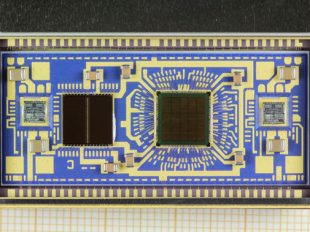
Hybrid device after the opening process
