MIL-STD-883 Method 2003 Solderability Testing employs the Dip and Look Method, requiring the following equipment:
- A solder pot is used to maintain the solder at a specified temperature.
- A steam aging equipment for ‘aging’ the samples prior to testing
- A dipping mechanism capable of controlling the rates of immersion and emersion and dwell time of the terminations.
- A microscopy system to facilitate the external visual inspection at a minimum magnification of 10x.
The general solderability test procedure consists of the following steps, following the MIL-STD-883 Method 2003:
- Proper preparation of the sample,s which must not include wiping, cleaning, scraping, or abrasive cleaning of the terminations to be tested.
- Aging of the samples in a steam ager, consisting on exposing the surfaces to be tested to water vapour for 8 hours and drying them, either by baking at 100ºC for no more than 1 hour in a dry atmosphere or air drying the mat ambient temperature for a minimum of 15 minutes.
- Proper application of flux to the terminations.
- Solder dipping by immersing the terminations in static solder at a uniform temperature of 245ºC +/- 5º C.
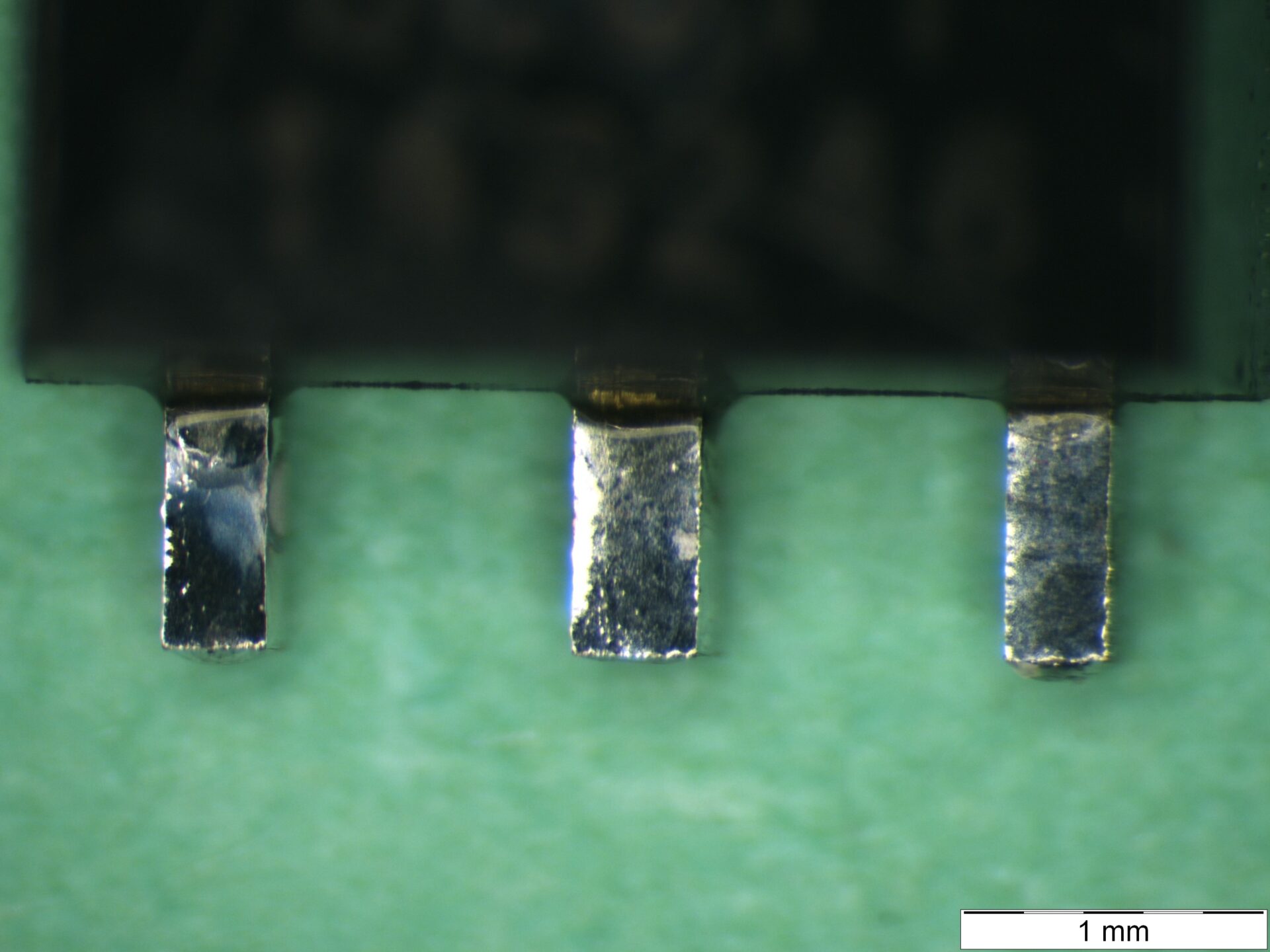
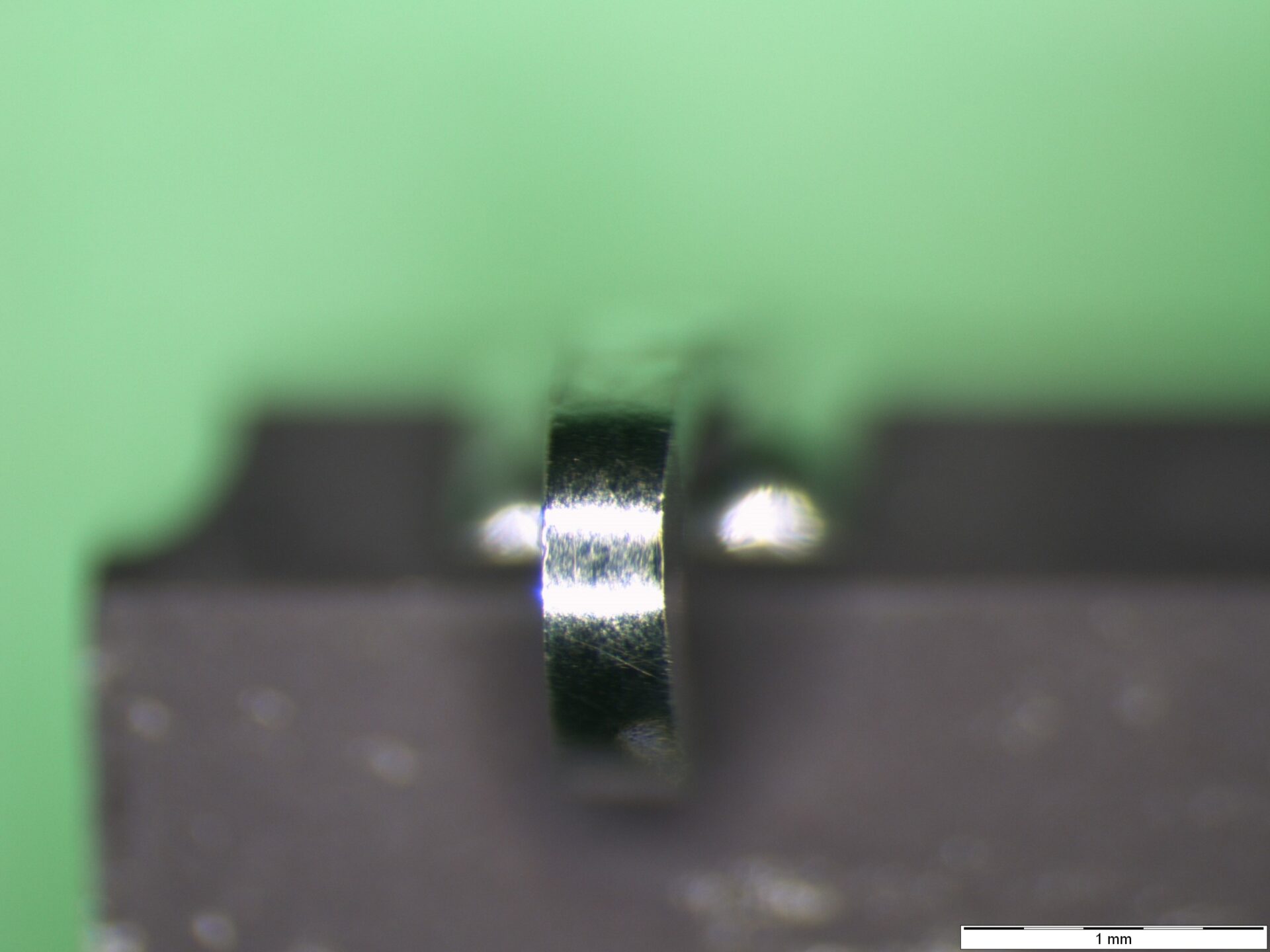
- Examination of the terminations at 10- 15x magnification.
Solderability Testing
The main criterion for acceptable solderability is 95% coverage of the dipped portion of the terminations by a new and continuous solder coating. Thus, pinholes, voids, porosity, nonwetting, or dewetting must not exceed 5% of the total dipped area.