A capacitor is a fundamental electronic component used to store energy in an electrostatic field, making it crucial for a variety of applications in electrical circuits. In this article, we explore what is a capacitor, its structure, how it works, and its key applications, such as energy storage, filtering, and signal coupling. Their understanding is essential for designing and optimizing electronic systems.
Applications – What is it good for?
Capacitors are common elements in electrical circuits with several applications and different requirements, such as:

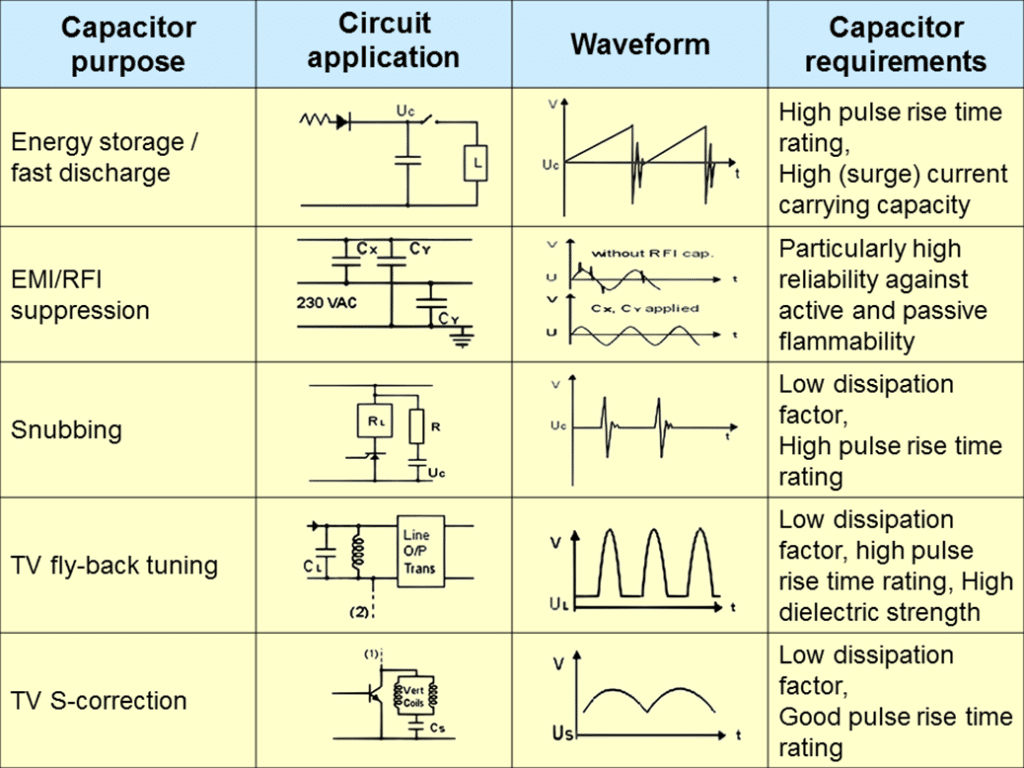
Fig.1. Typical applications overview table
Capacitor technologies
Comprehensive capacitor technologies differ in features, behavior, and range of electrical parameters covered. The most common capacitor technologies include:
- Air/Vacuum
- Aluminum
- Ceramic
- Film
- Tantalum and Niobium
- Silicon
- Supercapacitors
The amazing fact about capacitors today is that they cover over 17 ranges! Of its main parameter – CAPACITANCE this is hardly achieved by any other components technology.
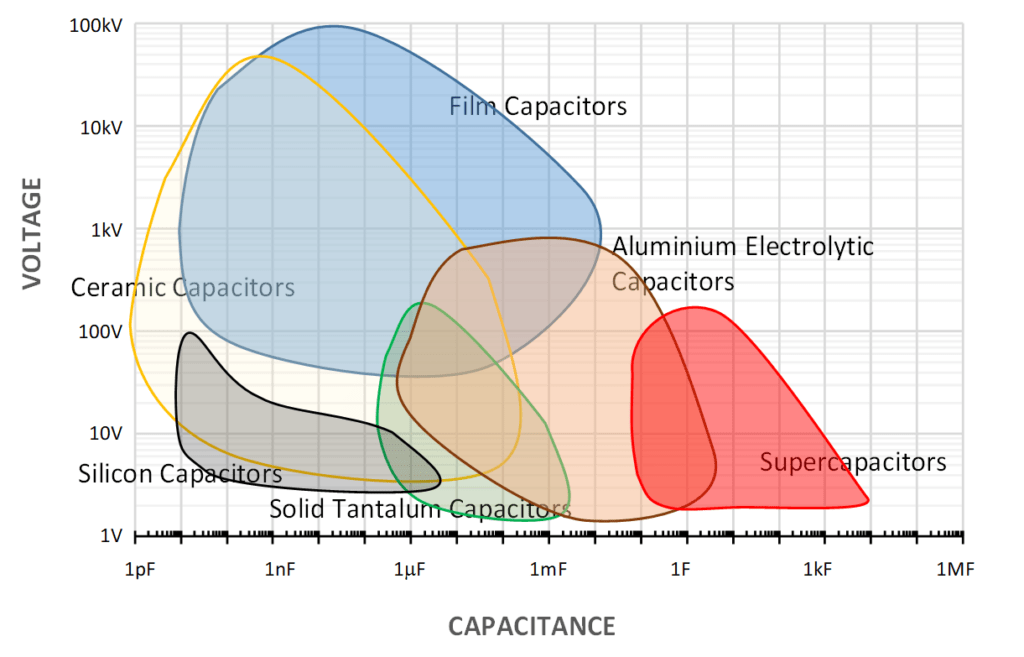
Fig. 2. The most common mass volume capacitor technologies capacitance vs voltage range;
source: EPCI
