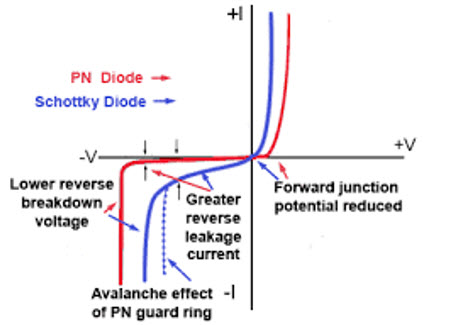
Silicon Schottky diodes are widely used in applications where high-speed switching is required and achieve more efficient systems due to their fast recovery time and low forward voltage. However, this type of diode has a lower reverse voltage (with a maximum typically around 100 V) than conventional rectifier diodes. Furthermore, the leakage current losses are higher.
The following graph shows the main differences between a Schottky diode and a PN junction diode:
SMV-PW Isabellenhüette Resistor
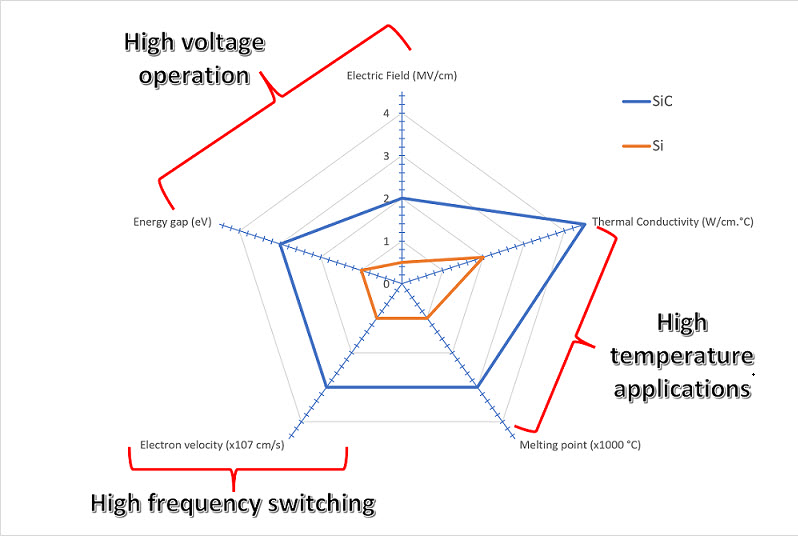
SiC benefits
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky diodes improve the characteristics of the silicon ones, getting a high reverse voltage, up to kilovolts, and bring 40 times lower reverse leakage current. Furthermore, SiC has high thermal conductivity, and the temperature has little influence on its thermal and switching characteristics.
More about SiC
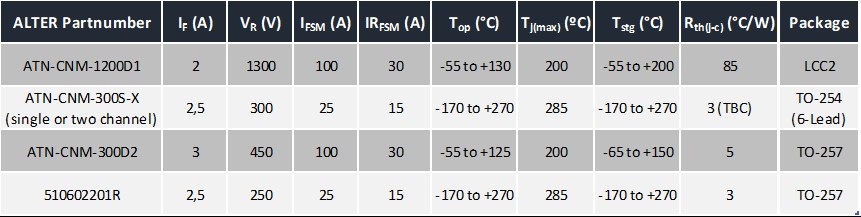
ALTER and CNM (Spain National Centre of Microelectronics) have developed SiC Schottky diodes with special packages that offer, in addition to SiC advantages, high junction temperatures, up to 330 degrees Celsius, and protons and gamma radiation tolerance. These components are a perfect solution for high-frequency or hard switching power space applications. They have been used successfully in ESA projects.
The available components and the main characteristics are summarized in the following table:
INCLUDED IN EPPL!
**Heavy ions tolerance under real flight bias conditions can be tested under request as already performed successfully for ESA-JUICE and ESA-BepiColombo mission!
